LED Technologies in Screens: Efficiency, Performance, and Applications
In recent years, LED (Light Emitting Diode) technology has revolutionized the screen industry with its energy efficiency, long lifespan, and high performance. Its low power consumption, brightness, and color accuracy have made it a fundamental element in modern visual media and display technologies. This article explores the advantages and disadvantages of different LED types, their technical characteristics, and their potential applications in screen technology.
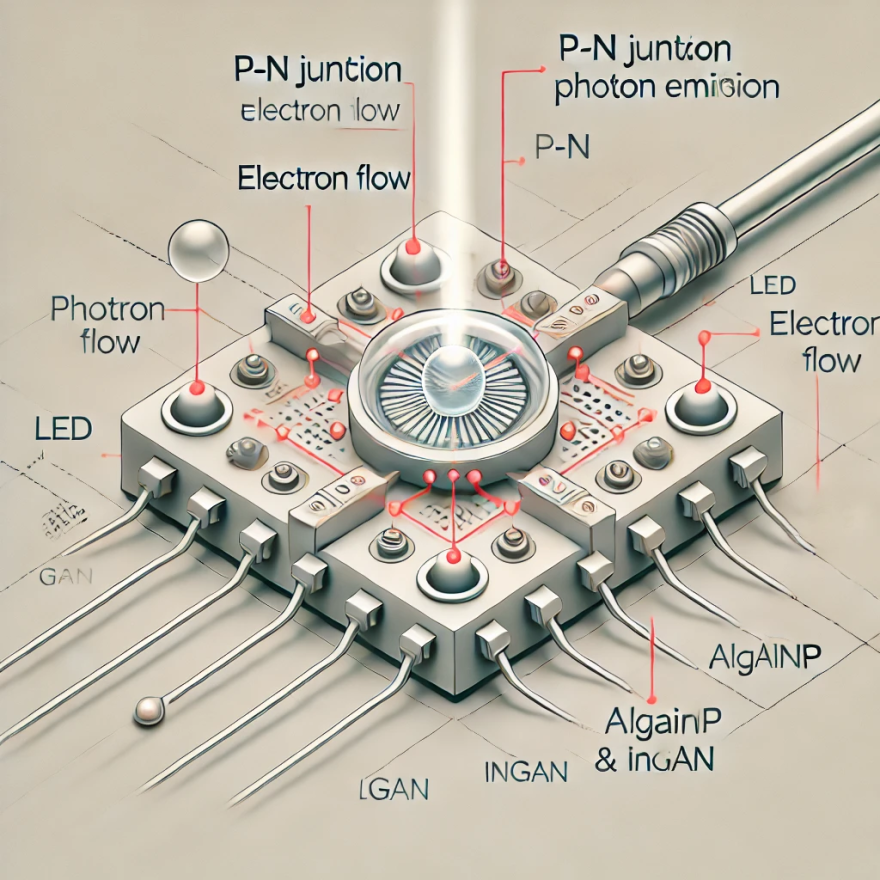
Basic Working Principle of LED
LEDs function by emitting light when electrical current passes through a semiconductor material. The electrons are excited, and energy is released as light. The light color and intensity depend on the semiconductor material's bandgap. This principle allows LEDs to produce various colors and brightness levels.
Types of LEDs and Their Features in Screen Applications
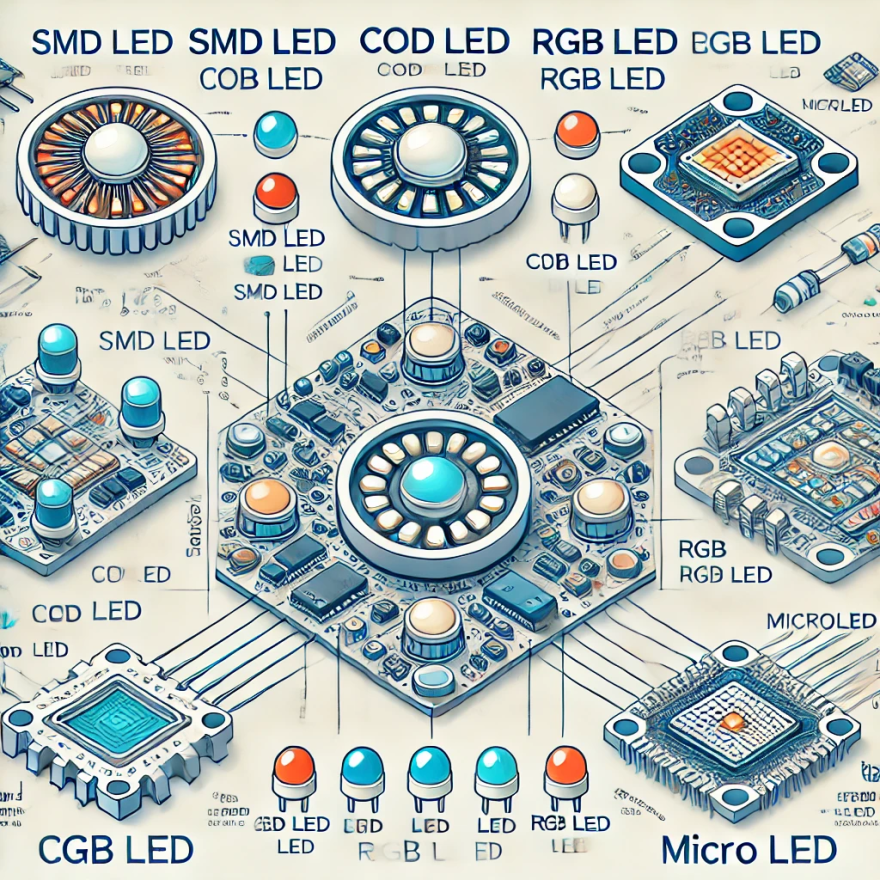
1. SMD (Surface-Mounted Diode)
- Description: SMD LEDs are compact, efficient light sources that are widely used in thin, lightweight screens due to their small size and ability to be mounted on surfaces.
- Advantages:
- High light efficiency and low power consumption, ensuring clear and bright images on screens.
- Compact design allows integration into slim screen technologies.
- Offers various color options, enriching the aesthetics of screens.
- Disadvantages:
- Thermal management issues can arise in high-power applications, affecting the screen's longevity.
- The small structure may present challenges in managing power and heat.
2. COB (Chip on Board)
- Description: COB LEDs consist of multiple LEDs placed closely together on a single board, providing high-intensity light. This type is ideal for large screens that require powerful lighting.
- Advantages:
- Provides high brightness, making it suitable for large or outdoor screens.
- Efficient thermal management extends the lifespan of the screen.
- Low power consumption with high efficiency reduces energy costs.
- Disadvantages:
- More expensive to produce, which increases overall costs.
- Limited use in small screen applications.
3. RGB LED
- Description: RGB LEDs combine red, green, and blue light to create a broad spectrum of colors, offering vibrant and dynamic visuals in displays.
- Advantages:
- Provides a wide color gamut, enabling rich and dynamic displays.
- High color accuracy improves visual quality.
- Precise control over light intensity enables flexible applications.
- Disadvantages:
- More expensive compared to other LED types.
- The use of multiple LEDs for color mixing can result in lower energy efficiency.
4. MicroLED
- Description: MicroLED technology uses tiny, independent LEDs for each pixel, allowing for high resolution and excellent color accuracy in displays.
- Advantages:
- Provides high resolution and brightness, creating sharp and clear images.
- Longer lifespan compared to OLED, as it does not rely on organic materials.
- Each pixel operates independently, offering superior contrast and color accuracy.
- Disadvantages:
- Higher production costs, making it less accessible.
- Large-scale production is not yet widespread.
Advantages of LED Technology in Display Applications
- Energy Efficiency: LED displays consume less energy while providing high brightness, reducing electricity costs.
- High Brightness and Color Accuracy: LEDs ensure vibrant, clear, and accurate color reproduction, making them ideal for visual media and digital signage.
- Long Lifespan: LED displays last significantly longer than other technologies, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
- Flexibility and Slimness: The thin nature of LEDs allows for integration into flexible display technologies, offering aesthetic and functional benefits.
The Future of LED Technologies in Screens
LED technology continues to evolve rapidly. Advances like MicroLED and OLED integration promise larger, more efficient displays. As light and color intensity become more precisely controlled, LEDs will play an even more critical role in creating dynamic and aesthetically pleasing screen solutions.
Conclusion
LED technology is shaping the future of displays with its energy efficiency, high performance, and long lifespan. The variety of LED types and their advantages in display applications make them integral to modern visual technology. As LED technologies continue to develop, they will drive innovation in the display industry, ensuring more efficient, sustainable, and high-quality solutions.


 English
English Français
Français Turkish
Turkish